

3, 14 Presence of posterior subtalar effusion is highly suggestive of an occult lateral process fracture. A lateral process fracture is best seen on a mortise view or Broden’s view, but the chip fractures are best seen on the lateral view just above the Angle of Gissane. Plain radiographs of the ankle in anteroposterior, lateral and mortise views should be performed routinely. 11, 12 A history of ‘ankle sprain’ and the presence of associated acute localized tenderness, swelling and haematoma around the tip of the lateral malleolus, along with painful range of motion, should raise the suspicion of a lateral process fracture. 7 Therefore, the movement and the positioning of the ankle joint at the time of injury appear to be more important than the type of footwear being used.Ĭlinically, up to 40% to 50% of lateral process fractures can be missed due to similar presentation as ankle sprains, even in the absence of distracting injuries.

12 However, Kirkpatrick et al reported a higher incidence of these fractures in snowboarders using hard boots as well. 11 One postulated reason behind their high incidence in snowboarders is the use of soft boots (70%), which results in more flexibility around the ankle joint leading to higher risk of foot and ankle injuries. Hawkins postulated that the avulsion of the lateral process caused by the pull of the lateral talocalcaneal ligament might be another contributing mechanism however, cadaveric and clinical studies do not clearly demonstrate this suggestion. 10 However, there is no disagreement that dorsiflexion plays the key role at the time of injury. 9 Funk et al, in another cadaveric study, suggested that a combined eversion and dorsiflexion might also play an important role resulting in these fractures. 8 Boon et al, in their cadaveric study, proposed that some degree of external rotation is also required to produce this type of injury. 5 This results in a lateral shift of the talar head, an upward shift of the lateral process of the talus on the posterior articular surface of the calcaneum and loss of congruity of the posterior articulation. The suggested mechanism is thought to be a consequence of forced dorsiflexion and inversion of a fixed pronated foot. Lateral process fractures are usually a result of high-energy injuries. Early diagnosis and timely management of these fractures help to avoid long-term complications, including malunion, nonunion or severe subtalar joint osteoarthritis.Ĭite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2018 3:85-92. Surgical treatment includes open reduction and internal fixation or excision of the fragments, depending on the size.įractures of the lateral and the posterior processes of the talus are uncommon but important injuries that may result in significant disability in cases of missed diagnosis or delayed or inadequate treatment. Non-operative treatment includes immobilization and protected weight-bearing for six weeks. There is a lack of consensus regarding optimal management of these fractures however, management depends on the size, location and displacement of the fragment, the degree of cartilage damage and instability of the subtalar joint. CT scans are helpful in cases of high clinical suspicion. The usual mechanism of injury is forced hyperplantarflexion and inversion causing direct compression of the posterior talus, or an avulsion fracture caused by the posterior talofibular ligament. The posterior process of the talus is composed of medial and lateral tubercles, separated by the groove for the flexor hallucis longus tendon.
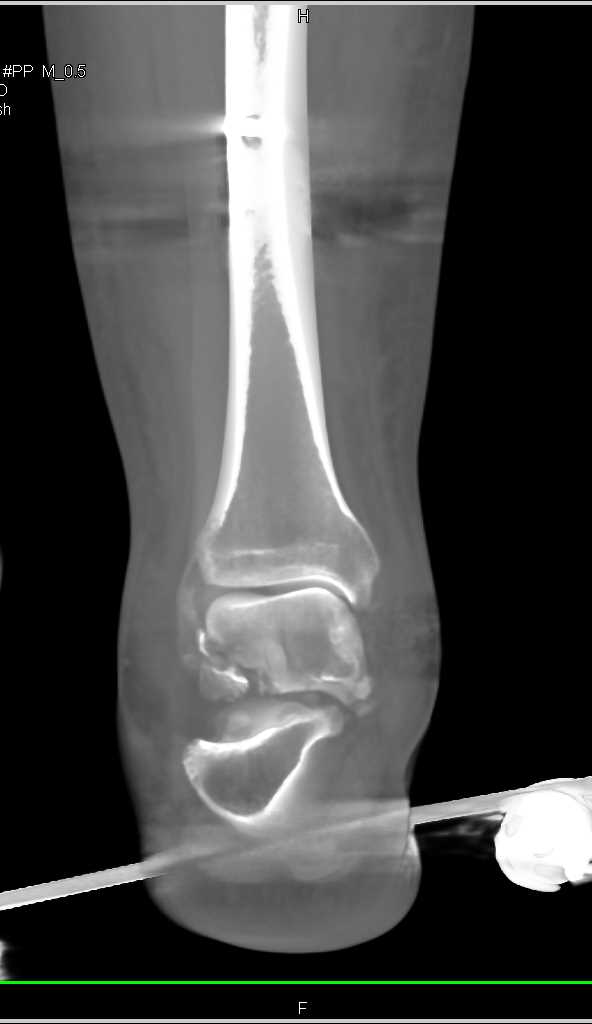
These are also commonly known as snowboarder’s fractures. Lateral process fractures are usually a consequence of forced dorsiflexion and inversion of fixed pronated foot. Missed fractures can lead to persistent pain and reduced function. Fractures of the lateral and the posterior processes of the talus are uncommon and frequently missed because of a low level of suspicion and difficulty in interpretation on plain radiographs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
